In virtually any firm, controlling revenue is vital for sustainable growth and economic stability. The revenue routine encompasses the entire method from the initial client relationship to the last collection of payment. It requires numerous phases and actions that eventually determine the financial health of the organization. In this informative article, we will explore the revenue pattern in detail, discussing its crucial parts, challenges, and strategies for optimizing financial performance.
Introduction to the Revenue Cycle:
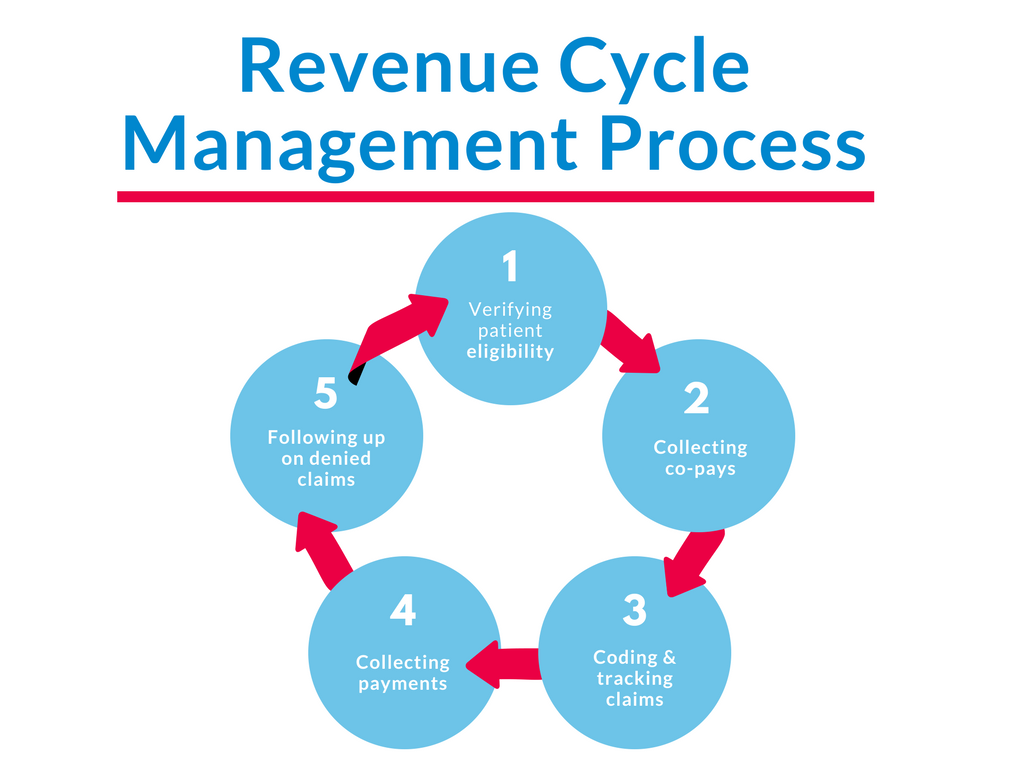
The revenue cycle shows the trip of revenue technology within an organization. It generally begins with cause technology and marketing efforts and advances through income, buy control, invoicing, cost variety, and reconciliation. Each point in the revenue cycle plays a crucial role in ensuring precise and regular revenue recognition.
Crucial Aspects of the Revenue Pattern:
a. Lead Era and Marketing: Getting possible consumers and producing consciousness about products and services or services.
b. Income and Customer Order: Transforming brings in to clients through effective sales techniques and negotiations.
c. Get Handling and Satisfaction: Getting and processing client instructions, ensuring precise item distribution or support fulfillment.
d. Invoicing and Billing: Generating invoices for services and products RCM service provider solutions made, including appropriate pricing and terms.
e. Accounts Receivable Administration: Tracking and collecting exceptional obligations from consumers, handling credit terms and cost terms.
f. Revenue Recognition and Confirming: Realizing revenue predicated on sales axioms and rules, ensuring precise financial reporting.
Challenges in the Revenue Period:
Managing the revenue pattern effortlessly is not without their challenges. Some typically common issues include:
a. Wrong Information and Documentation: Incomplete or data can result in delays in invoicing and payment collection.
b. Billing and Code Problems: Problems in billing or development can result in cost rejections or setbacks, impacting income flow.
c. Timely and Powerful Conversation: Insufficient distinct communication between departments can cause delays or misunderstandings in the revenue cycle.
d. Complex Cost Methods: Working with varied payment strategies, handling expenses, and reconciling transactions may be time-consuming and error-prone.
e. Conformity and Regulatory Requirements: Adhering to industry-specific rules and sales standards can be complex and need ongoing monitoring.
Techniques for Optimizing the Revenue Pattern:
To maximize economic achievement and ensure a smooth revenue cycle, organizations may implement the next techniques:
a. Improve Techniques: Recognize bottlenecks and inefficiencies in the revenue pattern, and improve techniques to reduce delays and increase productivity.
b. Embrace Engineering: Apply sturdy revenue pattern administration pc software and automation tools to enhance accuracy, pace, and efficiency.
c. Enhance Knowledge Accuracy: Purchase knowledge validation and quality get a handle on methods to decrease problems and errors in customer information and billing details.
d. Increase Communication and Cooperation: Foster efficient transmission and relationship between divisions involved in the revenue period to decrease misconceptions and delays.
e. Check Key Efficiency Indicators (KPIs): Identify and monitor relevant KPIs such as times income fantastic (DSO), series prices, and revenue development to evaluate and increase financial performance.
f. Staff Teaching and Knowledge: Give constant instruction and education to employees active in the revenue period to ensure a heavy knowledge of processes, conformity, and most readily useful practices.
Realization:
The revenue pattern is a crucial aspect of economic administration and organizational success. By understanding the important thing components, issues, and employing efficient techniques, agencies may improve their revenue routine, enhance money movement, increase customer care, and achieve long-term economic stability. Continuous monitoring, adaptation to business changes, and a commitment to process improvement are important for agencies to flourish in today’s aggressive business landscape.
